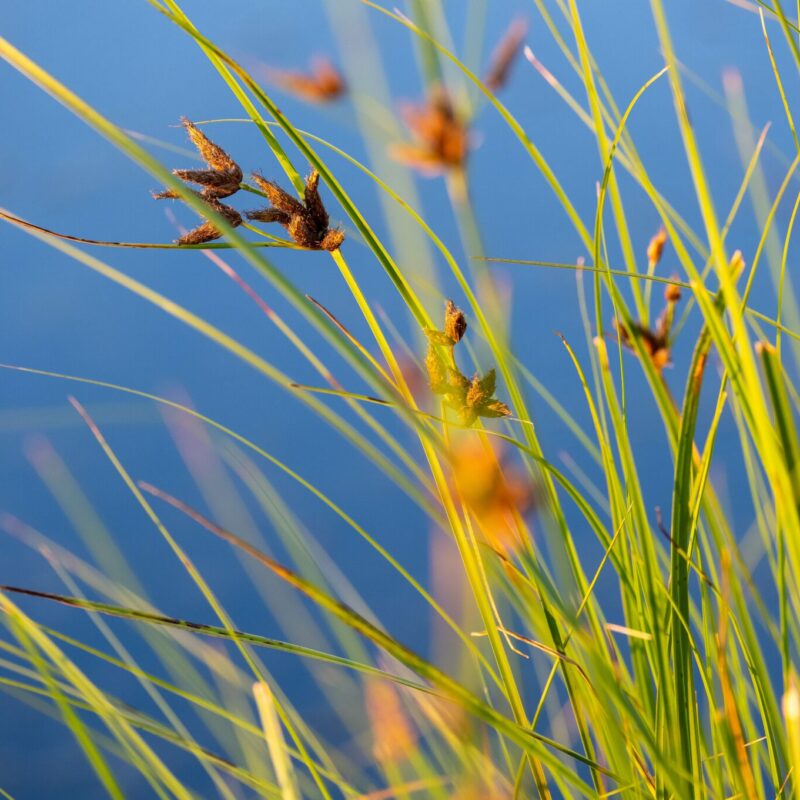
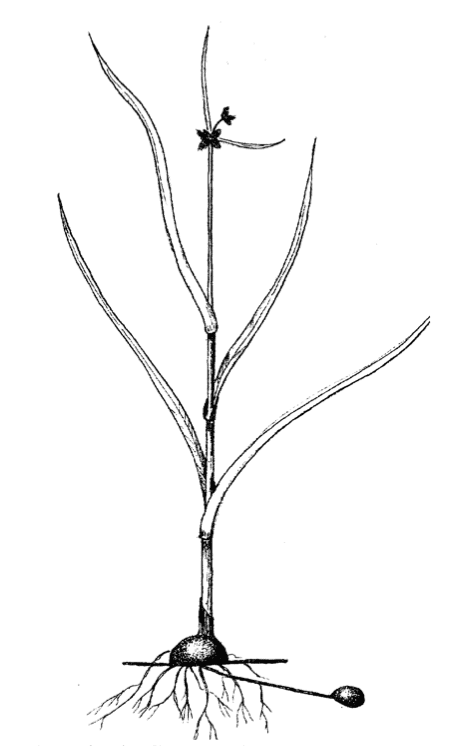
Alkali Bulrush
- Scientific name: Bolboschoenus maritimus
- A perennial riparian species
- Common in marshes, pond margins, wetlands
- Heavily rhizomatous
- Not palatable for livestock and big game
- Waterfowl utilize the stems for nesting cover
Min. to Max. Annual Precipitation
40in.
Average Max. Height
Alkali Bulrush (Bolboschoenus maritimes) is a perennial riparian species for in marshes, transient wet areas, pond margins, wetlands and brackish waterways. It is heavily rhizomatous. Alkali Bulrush is an important plant for waterfowl. Adapted to alkaline and salty sites. It forms large dense stands in alkaline or saline sites. Alkali bulrush (Bolboschoenus maritimes) can grow in soils with a pH of up to 9.0, and soil textures from fine clays to silt loams to sands.
For quick plant facts please click on the “Quick Plant Facts” tab.
General Description:
Alkali Bulrush (Bolboschoenus maritimes) is a perennial riparian species for in marshes, transient wet areas, pond margins, wetlands and brackish waterways. It is heavily rhizomatous. Alkali Bulrush is an important plant for waterfowl. Adapted to alkaline and salty sites. It forms large dense stands in alkaline or saline sites. Alkali bulrush (Bolboschoenus maritimes) can grow in soils with a pH of up to 9.0, and soil textures from fine clays to silt loams to sands. It can survive periods of total inundation of up to 1 m deep. It tends to spread and reproduce when the water table is within 10 cm of the surface. Alkali bulrush can occur on freshwater sites, but is usually a pioneering species that will be replaced over time with more permanent species. It is spread by seed and rhizome growth. This species is fairly resistant to fire which will increase its production and protein content.
As a pioneering species, it will provide protection from wind and wave erosion especially for newly exposed soil. The rhizomes also form a matrix for many beneficial bacteria, making this plant an excellent choice for wastewater treatment.
Common Names: Sea clubrush, Cosmopolitan bulrush, Saltmarsh bulrush, Bayonet grass
Uses:
Livestock and big game will rarely use this species. Palatability is low. Waterfowl will utilize the seed and use the stems for nesting cover. Muskrats and beaver will eat the rootstocks and young shoots. They will also use the shoots for building material.
Alkali Bullrush (Bolboschoenus maritimes) can be used for the following conservation issues: erosion control, constructed wetland System applications, wildlife food and cover, wetland creation and restoration, and for improvement of plant diversity in wetland and riparian communities.
Planting Conditions:
Alkali Bulrush prefers high pH soils (7.5-9.0) It grows best in heavy clay, silty, and muddy bottoms. It competes best in low nutrient soils. It thrives in shallow, standing water. It best to have upwards of 6″ of water for establishment. Established plants can handle upwards of 18″ standing water. It can survive in seasonally dry periods once it is established. It is ideal to plant in full sun areas.
Grows 2 to 5 feet tall. Typically, the water will be high in the spring and decline throughout the growing season to within 1 m of the surface in the fall. Water levels can be managed to either enhance or reduce spread as well as control terrestrial weeds.
Establishment:
Best time to plant is spring time when the soil is warm. Clear any competition before planting. The warmer temperatures and moisture helps break dormancy. Keep soil saturated with water (0-3″) for the first 4-8 weeks. Avoid deep flooding though as too much water can result in poor germination. Once the shoots appear you can add more water (6-12″ gradually). Don’t let the soil dry out. Thrives in soils that are 7.5-9.0 pH.Plant 2-4 inches deep in mud or high water table soils. They spread aggressively by their root systems.
Germination takes about 1-3 weeks. At 4-8 weeks the roots begin to really form (keep water shallow) By mid summer plants will have a thicker stem and begin spreading. By year 2 your stand will have expanded and fills in thickly.
Seeding Rate:
10-15 pounds per acre
Alkali Bulrush NRCS Plant Guide and Fact Sheet
Alkali Bulrush NRCS Plant Guide and Fact Sheet
PDF version of NRCS Plant Guide & Fact Sheet
Prepared By & Species Coordinator Chris Hoag, USDA NRCS Idaho Plant Materials Center, Aberdeen, Idaho
Helpful Links
Additional information about this product can be found on the academic websites linked below.
Synonyms
Many plants have more than one common and scientific name. We've listed a few of them below.
- Alkali Bullrush
- Bolboschoenus maritimus
- Sea Clubrush
- Cosmopolitan Bulrush
- Saltmarsh Bulrush
- Bayonet Grass
Who is Great Basin Seed?
Great Basin Seed is a seed company that specializes in seed sales and consultation for home, ranch, farm, range and reclamation. We have been a leader in the seed industry since 1974.
Our History
We've been in the seed business since 1974.
What We Offer
We offer seed for home, farm, ranch, range and reclamation projects.
Meet the Gang
We have the best employees in the world! We are proud of the work they do, and trust them to serve you!
Right: Company founder Lloyd and his wife Paula Stevens in a wildflower seed production field circa 1977
Quick Plant Facts
| Common Name: | Alkali Bulrush |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name: | |
| Old Scientific Name: | |
| Lifespan: | |
| Origin: | |
| Plant Type: | |
| pH Tolerance: | |
| Min. Precipitation | 25 Inches or more |
| Seed Count | 170,000 seeds/lb. |
| Growth Height: | |
| Root Form | Sodformer |
| Sowing Rate | 8 PLS lbs. per Acre |
| Best Sowing Time | Spring, Fall, or early Sumer |
| Max Sowing Depth: | |
| Growth Season: | |
| Sun & Shade Tolerance: | Shade Intolerant |
| Plant PDF File | scma.pdf |
| Hardiness Zones: |